Whey Protein vs Collagen: What is the difference?
Whey protein and collagen are two of the most popular supplements in the health and wellness world. Outside of those, collagen and protein are becoming quick and convenient options for those looking to improve their daily diets and ensure they get the nutrients their bodies need.
Due to their immense popularity, many ask, “Is collagen as good as whey?” To answer that and other questions, let’s break down what collagen and whey protein are, what they do, and how to take them.
What is whey protein?
Manufacturers make whey protein from whey, the watery part of milk that separates from curds during cheese-making. Have you ever noticed liquid floating on top of your yoghurt? That’s whey.
Although cheesemakers once discarded whey during the cheesemaking process, people now value whey for its role in producing whey protein. Producers pasteurise the whey, then concentrate and isolate the protein using membrane filtration or ion exchange technology. The end product is whey protein — the powder many enjoy in their shakes and protein bars.
There are three common types of whey protein:
- Whey protein concentrate (WPC): Contains low levels of fat and carbs.
- Whey Protein Isolate (WPI): WPIs undergo further processing to remove all but a very small amount of fat and lactose .
- Whey protein hydrolysate (WPH): A “predigested” form of whey protein that has undergone hydrolysis, a necessary process for the body to absorb protein.
Find out more about the differences between WPC and WPI.
How to use whey protein
Historically, whey protein was consumed purely to improve athletic performance and build lean muscle. However the landscape and understanding of protein needs and it’s benefits has evolved over recent times, with many people now actively increasing their daily protein intake to support health and wellness goals. How much you need, however, relies on your goals, activity level, age and overall lifestyle.
While the general Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for protein is 0.8g per kg of body weight, this applies mainly to those with a sedentary lifestyle. The protein requirement is higher for individuals with an active lifestyle and often many people will benefit from a higher protein intake.
The increase is typically between 1.2 and 2g of protein per kg of body weight daily for those following a healthy and active lifestyle. Age also plays a role, as older adults may need more protein to maintain muscle health due to age-related muscle loss, such as sarcopenia.
People enjoy whey protein as a protein shake, smoothie, or just with milk or water. Many also add whey protein powder to meals and snacks. Some popular recipes include:
- Banana whey protein pancakes
- Chocolate orange protein cake
- Whey protein chocolate pudding
- Dark chocolate protein truffles
What is collagen?
Collagen is an important protein that builds and maintains the connective tissue in our muscles, skin and bones. It comprises amino acids, zinc, copper, vitamin C and manganese.
There are 28 types of collagen, but the five most common are:
- Type I: Makes up 90% of the body’s collagen and provides structure to your skin, bones, tendons and ligaments.
- Type II: Found in elastic cartilage and provides joint support.
- Type III: Located in muscles, arteries and organs.
- Type IV: Found in layers of your skin.
- Type V: Located in the cornea of your eyes, some layers of skin, hair and placenta tissue.
How to use collagen
As we age, typically beginning in our mid-20s, collagen production declines at 1% per year. This decrease accelerates in later decades, leading to visible signs of ageing like wrinkles, sagging skin, and joint discomfort. Experts within the beauty industry have long touted collagen’s benefits, and now specialists in other fields are beginning to understand its untapped potential.
There are no official guidelines regarding how much collagen to take daily. However, a 2019 review of clinical studies found that 2.5 to 15g of collagen per day may be safe and effective for results.
Collagen supplements are often enjoyed as collagen protein powder or in gummies, tablets, or capsules. Many enjoy collagen powder mixed into cold water, milk, smoothies, or juice blends.
What is the difference between collagen and protein?
There are key differences between collagen vs. whey, including definition, function, and sources:
- Definition: Collagen is a specific type of protein, whereas protein refers to a general macronutrient composed of amino acids. Collagen contains a specific blend of amino acids, while protein can comprise a general blend.
- Function: Collagen provides structural support, while protein has a broader range of functions, including building muscle and supporting the immune system.
- Sources: Collagen is found in animal-based products such as animal bones and cartilage. Protein is found in various food sources, including meat, dairy, eggs, nuts, lentils, beans and legumes.
What are the benefits of whey protein?
Protein is often called the ‘building block of life,’ and regular intake — whether from whole foods or protein powder — provides numerous health and wellness benefits.
Improves muscle health
Protein is one of the most studied supplements in the world, and studies show that eating increased amounts of protein can help improve the health of your skeletal muscle, which is especially important as we get older.
Improves feelings of fullness
Studies show that meals high in protein help to keep you feel fuller for longer and reduces cravings. Protein reduces cravings by increasing PYY and GLP-1 peptides, which signal feelings of fullness to the brain.
Boosts your metabolism
Protein intake boosts your metabolism for a short period as your body uses calories to digest nutrients. This process is known as the thermic effect of food (TEF). Not all foods produce this effect, but protein has a higher TEF than fat or carbohydrates. Some studies show you can burn up to 100 more calories daily with a high-protein diet.
What are the benefits of collagen?
Like protein, collagen provides a range of benefits for the body.
Might prevent bone loss
Your bones primarily comprise collagen, which decreases in the body as you age. This decline in collagen reduces bone mass and could lead to conditions such as osteoporosis. Research suggests that collagen supplements may inhibit bone deterioration.
May promote heart health
Collagen supplements may reduce the risk of heart conditions as the protein provides structure to arteries. Without enough collagen, arteries become less flexible, which could lead to atherosclerosis. An increased daily intake of collagen could reduce artery stiffness.
Might improve skin health
Collagen is essential for skin health, especially for maintaining elasticity and hydration. Several studies show that collagen peptides or supplements may help slow skin ageing and reduce the appearance of wrinkles and dryness.
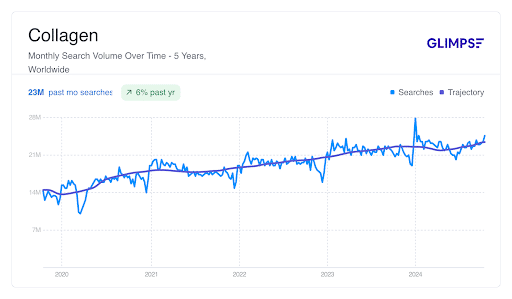
How popular is collagen?
Our research shows that 23 million people worldwide search for collagen monthly, a growth of 6% from October 2023 to October 2024. But why is this?
As consumer trends evolve, more people turn to collagen for health concerns like joint health and muscle recovery. People are also looking to improve their daily diets and find tasty, convenient options that fit with their lifestyles. Even celebrities, such as Jennifer Aniston, Kourtney Kardashian, Halle Berry and Kate Hudson swear by it.
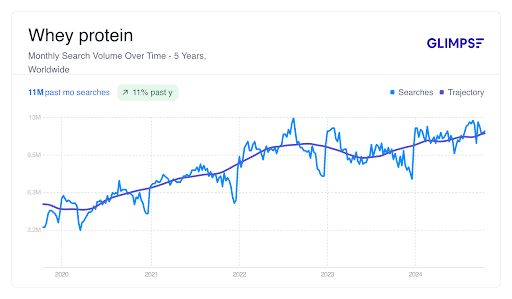
In addition to collagen, products that promote overall well-being are becoming increasingly popular. An example is whey protein, which has seen an 11% increase from October 2023 to October 2024.
Is collagen protein as good as whey?
Collagen and whey protein are great supplements for lifestyle and wellness, although they have slightly different purposes. Whey protein is a better source when looking to increase your dietary protein intake for nutritional value.
On the other hand, collagen might be a supplement for those looking for better joint health, skin elasticity, or overall wellness. As collagen production decreases as we age, it might also be an option for those heading into their late 40s.
As a result, many people opt to add both supplements to their diets, depending on their lifestyles and health goals. Ultimately, your supplement choice should align with your goals, needs and preferences. We even have bundles on offer that include some of our best product pairings with Collagen, Complete Wellness Bundle, and our Wake up & Glow Bundle.
Alternatively, both collagen and whey protein are available on our website as individual offerings.